 |
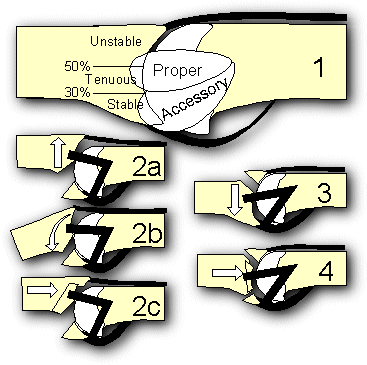
Fig. 3. Proximal interphalangeal joint
fracture dislocation patterns. Stability or instability of the joint after
dorsal or a volar fracture depends on the relative position of the fracture
line to the collateral ligaments (1.) . Palmar fractures may be associated
with dorsal subluxation (2a.), "hinge" motion rather than normal joint
gliding (2b.) or a combination of central impaction, dorsal and proximal
migration (2c.). Dorsal fractures are less common, and may be associated
with palmar subluxation (3.) or severe comminution (4.). |

