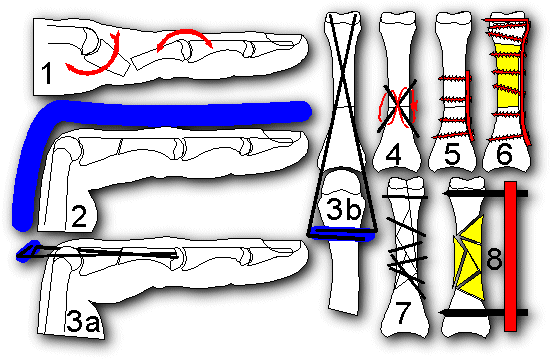
| Fig. 5. Proximal phalanx fracture fixation. Typically, fractures of
the shaft of the proximal phalanx displace in an apex volar pattern (1.).
Depending on the patient and the fracture patterns, these may be treated
with dorsal extension block splinting (2.), percutaneous intramedullary
pins, here augmented by bonding the protruding ends together to form an
external fixation construct for additional stability (3a,b.), open reduction
with pins, compression wires or mini plates (4,5.). Extreme comminution
or segmental bone loss may require primary segmental bone grafting (6.),
ingenious internal (7.) or external fixation (8.) |